Learning in PYP

We have a well-designed curriculum that is a mix of academics, creativity and personality development. It makes the learning enjoyable and brings out the best in children. We follow the IB-PYP curriculum for Grades Nursery to V. It is an inquiry based, trans-disciplinary approach practised globally.
Primary Years Programme
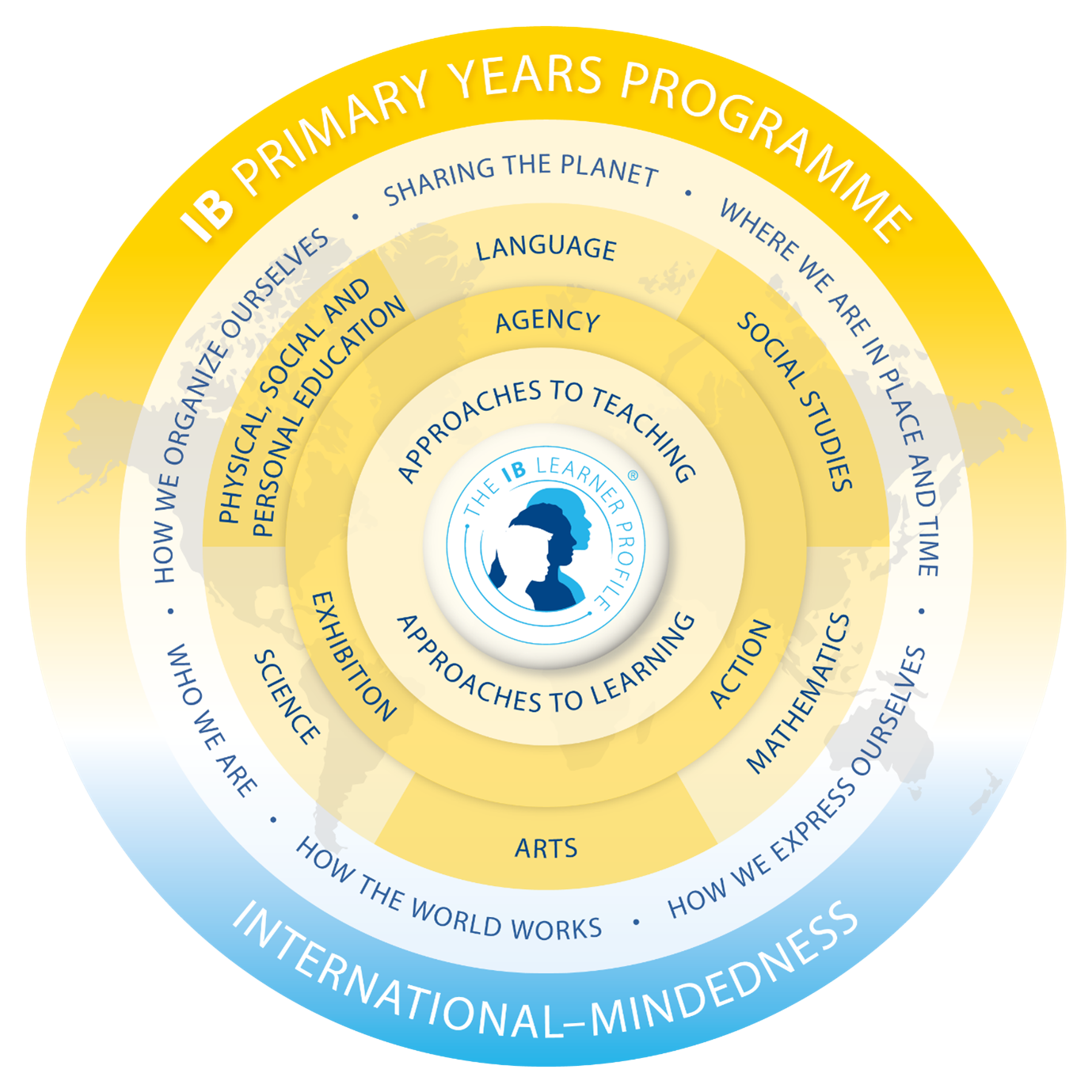
The Primary Years Programme (PYP) is designed for students aged from
three to eleven years. It is a philosophy, a curriculum framework and a
methodology accredited by IBO (Geneva Switzerland).
The PYP strives for a balance between the search for understanding, the
acquisition of essential knowledge and skills, the development of
positive attitudes and the opportunity for positive action. In terms of
achieving this balance, the PYP emphasizes five components of the
written curriculum.
Concepts SkillsAttitudeKnowledgeAction
Concepts- powerful ideas which have relevance within and across the disciplines and which students must explore and re-explore in order to develop understanding.This includes Form, Function, Causation, Change, Connection, Perspective, Responsibility and Reflection.
What is it like?
How does it work?
What are the points of view?
Why is it like it is?
How is it changing?
How is it connected to other things?
What is our responsibility?
Skills- the things the students need to be able to learn in an ever changing, challenging world like Thinking skills, Research skills, Social skills, Communication skills and Self-Management skills
Acquisition ofknowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, Evaluation, Dialectical thought and Metacognition.
Accepting responsibility, respecting others, Cooperating, Resolving conflict, Group decision- making, adopting a variety ofgroup roles.
Listening, Speaking, Reading , Writing, Viewing, Presenting and Non-verbal communication.
Gross motor skills, Fine motor skills, Spatial awareness, Organization, Time management, Safety, Healthy lifestyle, Codes of behavior and Informed choices.
Formulating questions, Observing, Planning, Collecting data, Recording data, Organizing data, Interpreting data, Presenting research findings.
Attitudes- dispositions which are expressions of fundamental values, beliefs and feelings about learning, the environment and people. This includes Appreciation, Commitment, Confidence, Cooperation, Creativity, Curiosity, Empathy, Enthusiasm, Integrity, Respect and Tolerance.
Appreciating the wonder and beauty of the world and its people.
Being committed to their own learning, persevering and showing self- discipline and responsibility.
Feeling confident in their ability as learners, having the courage to take risks, applying what they have learned and making appropriate decisions and choices.
Cooperating, collaborating, and leading or following as the situation demands.
Being creative and imaginative in their thinking and in their approach to problems and dilemmas.
Being curious about the nature of learning, about the world, its people and cultures.
Imagining themselves in another’s situation in order to understand his or her reasoning and emotions, so as to be open-minded and reflective about the perspectives of others.
Enjoying learning and willingly putting the effort into the process.
Thinking and acting independently, making their own judgments based on reasoned argument, and being able to defend their judgments.
Being honest and demonstrating a considered sense of fairness.
Respecting themselves, others and the world around them.
Being sensitive about differences and diversity in the world and being responsive to the needs of others.
Knowledge- significant, relevant, subject matter we wish the students to explore. This includes Who we are, Where we are in place and time, How we express ourselves, How the worlds works, How we organize ourselves and Sharing the planet.
An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures; rights and responsibilities; what it means to be human.
An inquiry into orientation in place and time; personal histories; homes and journeys; the discoveries, explorations and migrations of humankind; the relationships between and the interconnectedness of individuals and civilizations, from local and global perspectives.
An inquiry into the ways in which we discover and express ideas, feelings, nature, culture, beliefs and values; the ways in which we reflect on, extend and enjoy our creativity; our appreciation of the aesthetic.
An inquiry into the natural world and its laws; the interaction between the natural world (physical and biological) and human societies; how humans use their understanding of scientific principles; the impact of scientific and technological advances on society and on the environment.
An inquiry into the interconnectedness of human-made systems and communities; the structure and function of organizations; societal decision-making; economic activities and their impact on humankind and the environment.
An inquiry into rights and responsibilities in the struggle to share finite resources with other people and with other living things; communities and the relationships within and between them; access to equal opportunities; peace and conflict resolution.
Action- The action component of the PYP can involve service in the widest sense of the word: service to fellow students, and to the larger community, both in and outside the school. Through such service, students are able to grow both personally and socially, developing skills such as cooperation, problem solving, conflict resolution, and creative and critical thinking. Moreover, these actions are ways in which the students exhibit their commitment to the attributes of the learner profile and to the attitudes that we seek to engender within the PYP classroom. In fact, the actions that the students choose to take as a result of the learning may be considered the most significant summative assessment of the efficacy of the programme.